Introduction
Water softeners are essential devices for maintaining high-quality water in various settings, including residential homes. They work by removing minerals such as calcium and magnesium, which can cause scale buildup and other issues. The typical residential water softener consists of a cylinder around 5’1″ feet tall with a 1-foot diameter, along with a brine tank for regeneration. By connecting these devices to the water supply, they effectively treat the water for the entire building, ensuring a continuous supply of softened water.
Function and Operation
Understanding how water softeners function and operate is key to maximizing their benefits and ensuring optimal performance in any environment. A water softener is designed to remove minerals, specifically calcium and magnesium, from water. These minerals are responsible for making water “hard,” which can lead to issues such as white residue on surfaces and reduced effectiveness in cleaning tasks. By removing these minerals, a water softener helps to prevent mineral buildup and improve the overall quality of water, making it more suitable for various household uses.
ULTRATEC Whole House Water Softening System
The ULTRATEC Whole House Water Softening System includes several key components to effectively soften water throughout the entire house. These components consist of:
- Bypass Valve
- Distributor Basket
- Power Supply
- Drain Elbow
- Brine Tubing
- Brine Tank Lid
- Pressure Tank
- Brine Tank Valve
Each of these components plays a crucial role in the operation and efficiency of the water softening system, ensuring the removal of minerals like calcium and magnesium to provide softened water for various household needs.
System Diagram and Components
The ULTRATEC Whole House Water Softening System diagram showcases how it effectively reduces water hardness throughout the entire household, ensuring soft water is supplied to all areas. Typically, water softener systems consist of three key components: the resin tank, the control valve head, and the brine tank. The control valve head is usually located atop the resin tank, with the brine tank positioned nearby and connected via tubing.
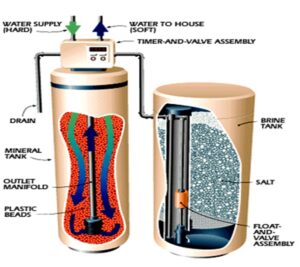
Ion Exchange Process
In a water softener system, water enters through the control valve head’s inlet and flows down into the resin tank. Within the resin tank, the water undergoes ion exchange with resin beads, where calcium and magnesium minerals are swapped for sodium, effectively softening the water. The softened water then travels up a central tube in the tank, passes through the control valve head, and exits the system through the outlet.
Regeneration Cycle
An essential aspect of the water softener system is the regeneration cycle. As the resin in the tank reaches its capacity limit from removing hardness minerals, it must regenerate to maintain effectiveness. The regeneration cycle involves stages like the brine draw stage, where brine from the brine tank replenishes lost sodium during the softening process. The regeneration cycle is typically programmed to occur at night when water usage is lower, ensuring uninterrupted softening operation and optimal performance of the system.
Purchasing Considerations
When buying a water softener, it is crucial to consider several factors to ensure it meets your specific requirements:
Size: Determine the appropriate size of the water softener based on the number of people in your household. A 1 cubic foot softener is suitable for one or two individuals, while a larger two cubic foot softener is recommended for households with three or more occupants for optimal performance.
Location: Select a location for the water softener that can accommodate both the resin tank and the brine tank. Ensure there is enough floor space and that the location is within 6 feet of a standard 120V electrical outlet and close to a drain, as the softener requires a drain line.
Flow Rate: Consult the softener’s manual to identify the maximum regeneration flow rate for your specific model. This information is essential for ensuring the water softener operates effectively and meets the needs of your household.
Maintenance
Water softeners are low-maintenance devices, but there are important factors to consider before purchasing one. It is crucial to ensure that the brine tank remains filled with salt for ongoing maintenance, with the amount of salt consumed varying based on the softener’s size and daily water usage. Regularly checking and refilling the brine tank as needed, along with annual cleaning to remove impurities, are recommended practices. The resin in the resin tank typically lasts around 8 years and should be replaced after this time. Some water softeners may require the entire tank to be replaced after a certain period. Opting for durable water softeners with fiberglass resin tanks and metal control valves is advisable.
Certification
When purchasing a water softener, look for the NSF certification to ensure it has undergone rigorous testing to effectively reduce water hardness. Only water softeners with NSF certification should be considered for your home. These devices are simple yet highly effective in treating hard water, preventing scale buildup, and protecting your plumbing system.
Conclusion
Consider factors such as system size, placement, and maintenance requirements when selecting a water softener. ULTRATEC offers a range of residential water softeners with high-quality features and NSF certification for sale. Investing in the ULTRATEC Whole House Water Softening System can provide the benefits of soft water in your home. This system is designed to remove minerals from water, improving water quality and preventing issues associated with hard water. Consider researching further and consulting with a water treatment professional to determine if the ULTRATEC system is the right choice for your home.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.